

The reproductive system is a marvel of biological engineering, responsible for the perpetuation of life across all species. In humans, as in many other organisms, this intricate system comprises a network of organs, glands, and hormones working in harmony to facilitate the complex processes of reproduction.
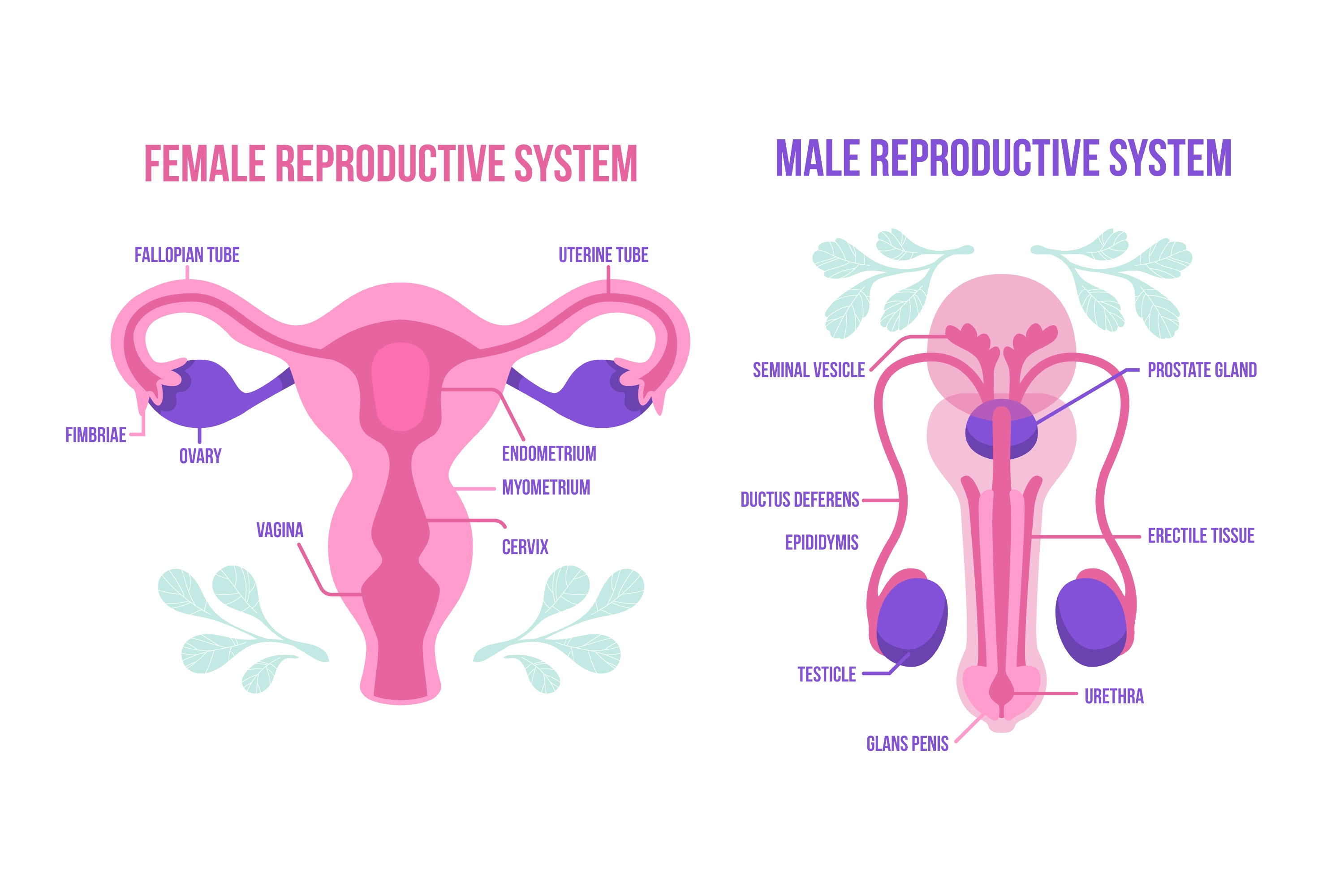
The male reproductive system consists of organs such as the testes, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and penis. Each of these structures plays a vital role in the production, storage, and delivery of sperm, the male gametes necessary for fertilisation.
Conversely, the female reproductive system includes organs like the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina. These organs are responsible for the production of eggs (ova), their transport through the reproductive tract, the reception of sperm, fertilisation, implantation of the embryo, and gestation.
The primary function of the reproductive system is the production of offspring, achieved through the fusion of male and female gametes during sexual intercourse. Beyond this fundamental role, the reproductive system also serves several other essential functions:
Despite its complexity and resilience, the reproductive system is susceptible to various disorders and conditions that can affect fertility, reproductive function, and overall health. Some common reproductive system disorders include:
The reproductive system is a marvel of evolution, essential for the survival and perpetuation of species. Understanding its anatomy, functions, and potential disorders is crucial for maintaining reproductive health and overall well-being. Through ongoing research, education, and healthcare interventions, we continue to deepen our understanding of this complex system, paving the way for advancements in reproductive medicine and improved quality of life for all.